 | 15 min read
| 15 min read
Aging, sun exposure and skin diseases cause cumulative changes to the skin and supporting tissues of the face:-
Sunspots and Hyperpigmentation (dark marks): Sun exposure can cause an increase in melanin production, resulting in dark patches or spots on the skin, commonly referred to as sunspots or age spots.
Visible blood vessels and redness on the face. Over time blood vessels can expand leading to the formation of spider veins or broken capillaries. Inflammatory skin diseases such as rosacea as well as sun exposure can exacerbate this.
Wrinkles, Fine Lines and Skin thinning: Over time, the skin's production of collagen and elastin is reduced, leading to a loss of elasticity and firmness. This results in the development of wrinkles and fine lines.
Scarring and textural change: Inflammatory skin conditions such as acne leads to scarring of the skin including the formation of pits, craters, or raised scars. As we age, scarring can become more noticeable, as the skin loses elasticity and firmness, and the appearance of scars can be further exacerbated by the loss of subcutaneous fat and bone. Aging also leads to changes in skin texture including the development of more prominent pores.
Benign and precancerous growths: Benign and precancerous skin growths are a common occurrence with aging, particularly on the face. Benign growths include things like moles, sebaceous hyperplasia, skin tags, and seborrheic keratoses. Precancerous growths include actinic keratoses.
Loss of subcutaneous fat and bone: As we age, there is progressive loss of fat and bone in certain areas of the face particularly the upper and mid face and this can lead to a hollowed appearance around the eyes and cheeks and deepening of the lines that run from the nose to the mouth.
Hair Loss: Hair loss is a common occurrence with aging, particularly in men, although it can also affect women. It can have a significant impact on a person's appearance and self-confidence.
When you attend the clinic I will systematically assess all of these concerns and I will agree with you to plan a course of treatments. This may include the following:
Topical treatments play an important part in the treatment of hyperpigmenation, acne, rosacea, fine lines and wrinkles and hair loss.
Daily sunscreen is essential to protect the skin from photoaging, skin cancer and pigmentation.
Retinoids have the ability to stimulate skin regeneration and cellular turnover. They work by binding to retinoic acid receptors in the skin, leading to an increase in collagen production, and the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. These processes result in the reduction of fine lines and wrinkles, improvement of skin texture, and reduction of hyperpigmentation.
Additionally, retinoids has been shown to be effective in treating acne by normalizing the desquamation of skin cells within hair follicles, reducing the formation of microcomedones, and decreasing inflammation. Consistent use can lead to smoother, clearer, and more youthful-looking skin.
Hydroquinone is primarily used to treat hyperpigmentation, including melasma, age spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. It works by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is responsible for the conversion of tyrosine to melanin – the pigment that gives color to our skin. By reducing the production of melanin, hydroquinone effectively lightens areas of excessive pigmentation and evens out the skin tone.
When used in combination, retinoids and hydroquinone can offer synergistic effects in treating various skin concerns. Tretinoin not only enhances the penetration of hydroquinone into the skin but also helps in the removal of existing melanin by increasing the rate of cellular turnover. This dual-action approach makes these topical treatments an effective option for patients seeking skin rejuvenation and regeneration.
Topical treatments for androgenetic alopecia (hair loss) in men include minoxidil and finasteride (which can both be taken orally). Topical minoxidil is also used for androgenetic alopecia in women and can be combined with oral spironolactone.
There are a range of other topical treatments available to address rosacea, pigmentation and skin aging and, if needed, these can be supplied in customized topical formulations.
Cryotherapy, minor skin surgery, and electrocautery are all commonly used treatments for benign and precancerous skin growths such as seborrhoiec keratoses and actinic keratoses on the face. Cryotherapy involves using extreme cold, typically through the use of liquid nitrogen, to freeze and destroy the growths. Skin surgery, such as shave removal or curettage, involves physically cutting or scraping away lesions such as harmless moles or seborrhoeic keratoses from the skin. Electrocautery involves using a high-frequency electric current to burn and remove smaller lesions such as areas of sebaceous hyperplasia (enlarged sebaceous glands).
Laser treatments are a mainstay of regenerative dermatology, offering targeted treatments for fine lines, textural change, laxity, scarring and pigmentary change.
Fractional laser treatments work by delivering focused beams of light energy to the skin, creating controlled micro-injuries that trigger the body's natural healing response. This process stimulates the production of new collagen and elastin fibers, which are crucial components of the skin's structural integrity. Fractional lasers can be subdivided into ablative and non-ablative lasers.
Ablative lasers: These lasers remove the outer layers of the skin, causing a more profound injury and promoting a more aggressive healing response. Ablative laser treatments, such as CO2 lasers, are effective in treating deeper wrinkles, scars, and severe sun damage. However, they come with a higher risk of side effects and a longer recovery period.
Non-ablative lasers: These lasers do not remove the skin's outer layers but instead target the underlying tissues to stimulate collagen production without causing significant damage to the skin's surface. Non-ablative laser treatments, such as the 1540nm Erbium glass laser, are typically used for treating mild wrinkles and more superficial scars.. They offer a more gentle approach with minimal downtime but may require multiple sessions to achieve the desired results.
Q-switched lasers: Q-switched lasers deliver high-energy pulses of light in extremely short durations (nanoseconds) allowing for the targeted destruction of pigmented lesions without causing thermal damage to the surrounding tissue. Q-switched lasers, such as Nd:YAG are highly effective in treating various pigmented lesions, including age spots and freckles
Pulsed-dye lasers: Pulsed-dye lasers (PDL) emit light in the yellow to red wavelength spectrum, selectively targeting haemoglobin in blood vessels. This specificity makes PDL highly effective in treating facial redness, prominent blood vessles and certain types of scars. PDL works by heating the blood vessels, leading to their collapse and eventual absorption by the body without causing significant damage to the surrounding skin.
Overall, laser treatments have become an essential component of regenerative dermatology, providing patients with non-invasive options for skin regeneration and rejuvenation. Often Dr Lynch will combine multiple lasers in a single treatment session.
Learn more about laser treatments
Toxins, such as botulinum toxin (Botox), are commonly used in facial rejuvenation to reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. Botox works by blocking the signals from the nerves to the muscles, which relaxes the muscles and reduces their ability to contract. This can help to smooth out wrinkles and prevent the development of new ones. Botox is typically used in areas such as the forehead, frown lines, and crow's feet around the eyes. The treatment is minimally invasive and typically involves a series of injections that take only a few minutes to complete. The effects of Botox usually last for several months before the treatment needs to be repeated. Botox injections can also be used in the lower face to relax the muscles that cause dynamic wrinkles, such as those around the mouth and chin.
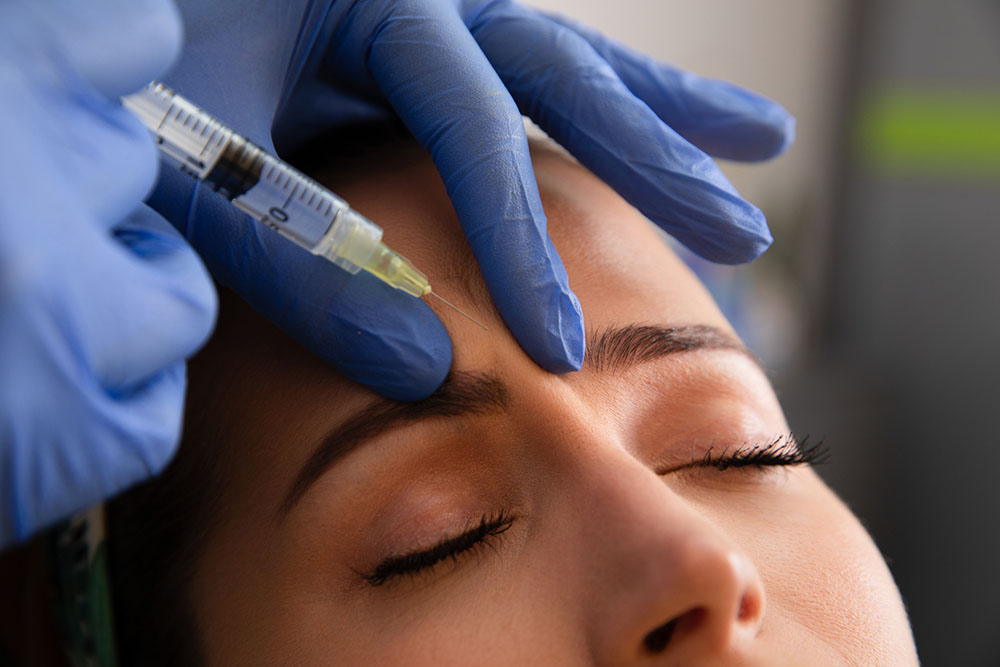
Dermal fillers and skin boosters are two types of cosmetic treatments that can help to improve the appearance of aging skin by restoring volume, hydration, and elasticity.
Dermal fillers are injectable substances that are used to restore lost volume under the skin surface and plump up the skin. They are particularly effective in restoring the age-related volume loss that affects the cheeks and midface. The most common types of dermal fillers are made from hyaluronic acid, a naturally occurring substance in the body.
Skin boosters are injectable substances that are used to improve the hydration and texture of the skin. They are injected into the outer layer of the skin and also typically contain hyaluronic acid or other substances that help to retain moisture and stimulate collagen production in the skin. Skin boosters are commonly used to improve the plumpness of the skin and the overall texture and tone.
Both dermal fillers and skin boosters can play a role in skin regeneration by improving the health and appearance of the skin. By restoring volume and hydration, these treatments can help to reduce the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and other signs of aging.
To book an in person consultation, enter your details below and my practice management team will contact you to schedule the appointment. Alternatively call 0203 389 6076 (calls are answered during working hours) or email: [email protected].